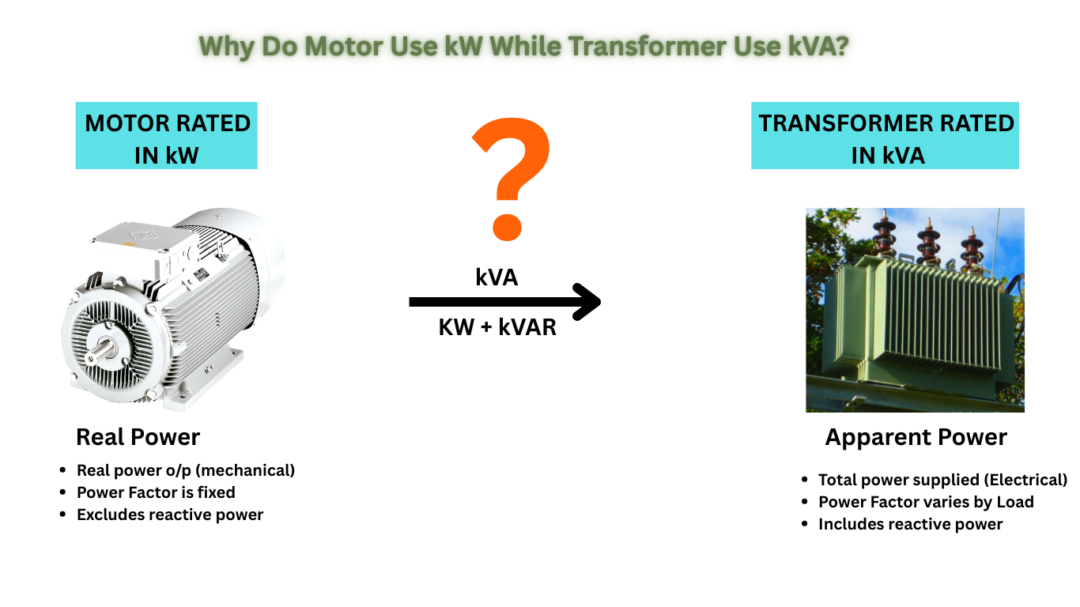
The difference between motors using kilowatts (kW) and transformers using kilovolt-amperes (kVA) comes down to how power is measured and the nature of their operation:
1. Motors (kW – Active Power)
– Motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy (work), and their useful output is real power (kW).
– Power factor (PF) plays a key role: Motors have a lagging PF (due to inductive windings), meaning not all the supplied apparent power (kVA) is converted into useful work.
– kW = kVA × Power Factor
Since motors are load devices, their rating focuses on the actual usable power (kW) they deliver, not just the total power drawn from the supply.
2. Transformers (kVA – Apparent Power)
– Transformers transfer electrical energy (they don’t convert it into mechanical work), so their capacity depends on **current and voltage handling (kVA = V × A).
– Power factor is determined by the load, not the transformer itself. A transformer must supply both real power (kW) and reactive power (kVAR) to the load.
– Since the PF varies with the connected load, transformers are rated in kVA (apparent power) to indicate their maximum current-carrying capability without overheating, regardless of PF.
*Key Takeaway*
– Motors (kW): Rated by useful mechanical power output (after accounting for inefficiencies and PF).
– Transformers (kVA): Rated by maximum electrical power they can transfer, since their output depends on the load’s PF.
*Example:*
– A 10 kW motor at PF = 0.8 draws 12.5 kVA (since kW = kVA × PF → kVA = kW/PF).
– A 10 kVA transformer can supply up to 10 kVA, but the actual usable power (kW) depends on the load’s PF (e.g., 8 kW at PF = 0.8).
Thus, motors are rated in kW (useful power), while transformers are rated in kVA (total possible power transfer capacity).