Table of Contents
The three main solar cell technologies are monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and amorphous. Each technology has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on cost and efficiency. Monocrystalline cells have the highest efficiency, followed by polycrystalline and amorphous cells. The efficiency of monocrystalline cells is higher because they are made from a single crystal, while polycrystalline cells are made from a mixture of different crystals, leading to lower efficiency. Amorphous panels are generally used for smaller devices like calculators, etc and their efficiency is much lower than monocrystalline and polycrystalline cells.
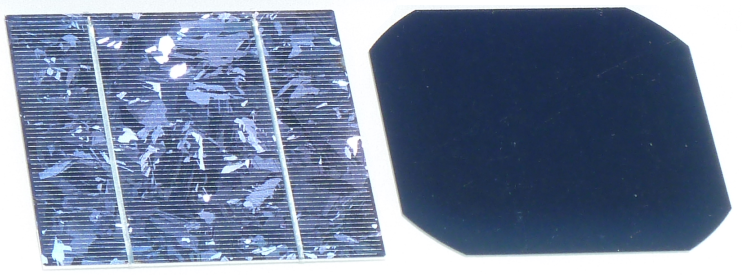
Mono-crystalline solar cell
The term “monocrystalline” refers to a solar cell made from a single crystal, resulting in higher efficiency compared to polycrystalline cells. Monocrystalline cells have a different physical appearance and are composed of a single crystal structure, which leads to higher efficiency. On the other hand, polycrystalline cells consist of a mixture of different crystals, resulting in misaligned atoms and varying efficiencies. Monocrystalline solar panels are used in solar power plant installations due to their higher efficiency, which allows for more power generation using less installation surface area. In comparison, polycrystalline panels have lower efficiency. Monocrystalline cells also perform well in low light and cloudy conditions, as well as during winter seasons, making them a preferred choice for areas with limited space, where high energy output is essential.

Fig : – Mono-crystalline Solar Cell
Advantage
- This have the highest level of efficiency at 15-23 % (also consider Brand)
- They require less surface of installation because of high efficiency
- It perform good in low light and cloudy winter season
- This solar cells last longer with life of more than 25 years
Disadvantage
- This is expensive in market
- During manufacturing it emits lots of waste
- With increase in temperature the performance get decreases
Poly-crystalline solar cell
As the name suggests, polycrystalline means multiple crystal structures compared to the single uniform crystal structure of monocrystalline panels. In polycrystalline panels, the ‘poly’ prefix means many crystals, indicating that they contain many small grains of crystals. They are actually made from casting cube-shaped structures from molten silicon. This method is known as ‘defined film-fed growth,’ in which a thin ribbon of polycrystalline silicon is created from molten silicon. Polycrystalline panels are cheaper than monocrystalline panels because they contain a mixture of different crystals, which makes them affordable for many vendors and customers. Regarding efficiency, polycrystalline panels range from 15% to 20%, with some brands offering more than 20%. However, they require more space for installation compared to monocrystalline panels. They are preferred when a large surface area is available for installation due to their affordability. However, their lifespan and efficiency degradation are slightly lower than monocrystalline panels. Physically, polycrystalline solar panels show a mix of crystals in their internal structure. When looking at the arrangement of atoms within the panel, the atoms are not aligned in the same direction due to the addition of different crystals, which affects the efficiency of the solar panel.”

Fig : – Poly-crystalline Solar Cell
Advantage
- The manufacturing process is cheaper then others
- cost of solar panel is also cheaper as compared to mono-crystalline
- For Big plants or solar parks the first preference is poly-crystalline
- At higher temperature it effects less in performance
Disadvantage
- It takes large surface as compare to mono-crystalline
- Efficiency is also less
Thin Film Cells
Thin-film solar cells are designed for flexibility, allowing them to be used in various applications for energy production. Although they are less efficient, they are still used for small-scale projects. These solar cells are made by depositing thin layers of silicon and glass, resulting in a very thin and flexible product that uses less than 1% of the silicon needed for crystalline solar cells. This reduction in raw materials and the less energy-intensive manufacturing process makes amorphous silicon cells much cheaper to produce, despite their reduced efficiency.